Blog Archive
-
▼
2009
(338)
-
▼
October
(133)
- Eye Blindness
- Facts on Smoking
- Aids Information
- Eight Ways to get chances of success of treatment ...
- Hypertension High Blood Pressure
- Part B drug proposal
- MRI of the Breast
- Medicine Nobel Prize 2009
- Ipphone
- H1N1 Disease
- Best Diet to Lose Weight
- Is Cancer Hereditary
- Not Afraid
- Heart Disease Risk Factor
- Sickle Cell Anemia Treatment
- Natural Killer Cells
- Aids Vaccine
- Sweet play a Role in Cancer Metastasis
- Down Syndrome Information
- Effect of Carbonation
- Vulvar cancer
- Vagina Cancer
- Cancer Uterus
- Thyroid Cancer Treatment
- Cancer of the Throat
- Cancer Testicular
- Rectal Cancer
- Prostatic Cancer
- Pharyngeal Cancer
- Pancreatic Cancers
- Ovarion Cancer
- Multiple Myeloma Cancer
- Mesothelioma Information
- Melenoma
- Lymphomas
- Lung Cancers
- Liver Cancer Survival
- Penis Pimples
- Genital Herpies
- Prostitis
- Syphilis Treatment
- Nongonococcal Urethritis
- Balanitis Treatment
- Reiters Syndrome
- Sickle Cell Anemia Symptoms
- Penile Prostheses
- Peyronie's Disease Treatment
- Priapism Treatment
- Smallpox History
- Tetanus Symptoms
- Toxoplamosis
- Trichinellosis
- Tuberculosis Disease
- Rabbit Fever
- Typhoid Disease
- Chicken Pox Virus
- West Nile Disease
- Yellow Fever Virus
- Cocaine Drug
- Penis Pain Due To Related Causes Of Diabetes
- Erectile or Impotence (Penis Disease)
- Penis Rashes,Lumps & Spots
- Combat Acne with Your MP3 Player
- Skin Facts
- Stretch Marks
- What is Medical Technology
- Sexual Desire May Be Revealed in Probe of Prairie ...
- cancel the serologicaltest of hepatitis B in physi...
- MERIAL INVESTS US $ 70 MILLION
- UK Prime Minister Message Joining Charity
- Popcorn Good For You
- Breast Cancer And Health Insurance In USA
- Breast Cancer Risks
- Body Building Secrets
- American Journal of Cardiology
- Penis Disorders
- Cancer of the Penis
- Diseases of Penis
- Genetic Baldness Test
- Latest Medical Equipment
- Medical Biogel
- MRI Equipment
- hemopurifier
- Obesity Solution
- Home Made Skin Recipes
- Treatment for Oily Skin
- Leukemia Cancer
- Skin Types
- Skin Care Information
- Skin Care Tip
- Tips for Skin Care
- Beauty Skin Care Tips
- About cholera
- Infectious Viruses
- Types Infectious Diseases
- Recent Health News
- Atrial Fibrillation Guidelines
- Atrial Fibrillation Guidelines
- HIV News
- Skin Care Lines
-
▼
October
(133)
Monday, October 19, 2009
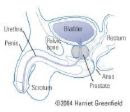
Prostitis:
Introduction: Prostatitis, and infection prostrate, or painful prostate
Description:
* The prostate gland in men, located between the rectum and bladder (where urine is stored), may become inflamed (swelling, irritation, and pain).
* This gland surrounds the neck of the bladder and urethra (tube that urine from the bladder in the blanks through the penis). Inflammation or prostatitis tends to stifle the urethra and obstructing the flow of semen and urine. Prostatitis can be acute (sudden) or chronic (over time).
Symptom:
* Acute:
1. Frequent urination
2. A feeling of the need to push urine out of
3. The flow of urine (the amount of urine)
4. Inability to empty the bladder completely
5. Fever
6. Chills
7. Pain or burning during urination (dysuria)
8. Frequent urination at night (frequent urination during the night)
9. Painful ejaculation
10. Lower back pain
11. Pain in the lower abdomen
12. Pain with bowel movement
13. Blood in the urine or semen.
14. Pain in the testicles
* Chronic:
1. The symptoms may be mild or absent.
2. Symptoms similar to acute form.
3. In the form of non-germ, fever and chills may be absent.
Causes:-
Of infection:
1. Such as coliform bacteria, false, Proteus, chlamydia and gonorrhea, and many others can cause inflammation of the prostate.
2. Bacteria may cause both acute and chronic forms.
* Cause inflammation:
1. And narrow or narrowing of the urethra may cause urine to back up (islands) and cause prostatitis.
2. Prostate cancer can be prevented or extend the neck of the bladder, causing urine leakage and result in about prostatitis.
3. Damage to the nerves that feed the prostate (ie, spinal disk) and tension in the muscles around the prostate can cause prostatitis.
4. The immune system - the body's natural defense system may play a role in inflammation of the prostate.
How Diognosis:
* Date:
1. Symptoms - when, and how severe.
2. Diseases - infections, etc..
3. Surgery - Cystoscopy recent
4. Habits - sexual habits
5. Family
6. Drugs
7. Sensitivity
* Medical exam:
1. May or may not have fever
2. May reveal the presence of warm, swollen and destruction when the doctor inserted his gloved index finger in the rectum in order to reach the study and prostration (rectal exam).
3. The groin area may be tender blocks known as the inguinal lymph nodes.
* Is collected urine samples (urine analysis - U / A) and pus may appear, the white blood cells and red blood cells.
* Urine culture (clean catch sample) is collected and sent to the laboratory where in 24-48 hours the offending bacteria (and its sensitivity to antibiotics factors) are identified.
* Have blood samples can also be done to the cultures.
* Prostate massage is useful in highlighting the dump, which contains the bacteria (not even antibiotics, has begun).
* At the causes of chronic non-bacterial and bacterial, U /, and can appear white blood cells and cells that contain fat droplets (oval fat bodies), but the bacteria may be absent. In all cases, and urine, and urine in the bladder, and prostate secretions should be sent for bacterial cultures.
* In the form of non-viable bacteria, and cultures negative bacteria, and not existing ones.
Risks Factor:
* Gender Male
Sexually active *
* Age - more than 50 (in the form of chronic)
* Urinary tract infections
* Acute prostatitis is a risk factor for the chronic form.
* Prostate stones
* Epididymitis - inflammation of the ducts that drain the testicles.
* Urethritis - inflammation of the urethra
* Manipulation or the introduction of the devices in the urinary tract (cystoscopy and catheterization)
* Infections in other parts of the body (for example, rectum)
The high levels of uric acid
Treatments:
* Rest in bed
* Fluid
* Cranberry juice may help
* Analgesics - Tylenol or Advil
* Stool
* Sitz baths will help with the pain and cramps.
* Antibiotics such as Septra assistance in the form of sharp.
* Ciprofloxacin for periods of a day (more than 3 months) and are often given to the chronic form.
* In the forms of non-bacterial - antibiotics are also tried
* If antibiotics do not heal, amputation surgery in the prostate or thermal (heat) by using the wave may be an option for non-acute forms of prostatitis.
* Avoid spicy foods, alcohol, and caffeine.
Suspection this condition:
* Contact your physician, especially if there is pain, fever, chills, or bleeding.
Similar conditions:
* Inflammation of the seminal vesicles - painful ejaculation
* Cystitis - inflammation of the bladder
* Prostatodynia - in young people, and produces symptoms similar to prostatitis
* Inflammation of the urethra
Labels: Penis Diseases
0 Comments:
Category
- Breast cancer (1)
- Cancer Forum (46)
- Depression and Exercise (17)
- Fitness Woman (14)
- Health Video (22)
- herbal remedies (63)
- Infectious Deseases (14)
- joint pain exercises (8)
- Latest Medical Technology (4)
- loose fat exercise (13)
- Penis Diseases (17)
- Pregnancy (6)
- Pregnancy Exercise (27)
- pregnancy tips video (21)
- skin care (15)
- World Health News (62)